ADSL, VDSL, And VDSL2: What Are They?
If you're curious about the definitions of ADSL, VDSL, and VDSL2, learn all the intricacies with our detailed guide now!

In today's rapidly digitizing world, communication and internet access have become integral parts of individuals' and organizations' daily lives. In this context, broadband communication technologies play a crucial role as one of the significant factors shaping users' internet experiences. Among these technologies, ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line), VDSL (Very High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line), and VDSL2 (Very High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line 2) stand out as important broadband communication protocols used to provide internet access.
ADSL, VDSL, and VDSL2 are known as digital subscriber lines with different speeds and capacities. They enable users to efficiently manage high-speed data transmission, online content consumption, and business processes.
In our article, we will focus on the fundamental principles, advantages, and usage areas of ADSL, VDSL, and VDSL2, providing depth to understand their importance in today's communication infrastructure.
So, without further ado, learn what ADSL, VDSL, and VDSL2 are in full detail with all their differences!
If WhatsApp notification not working, learn the solution immediately with this content!
What is ADSL?

ADSL stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. It is a modem technology that enables high-speed data, voice, and video communication simultaneously over existing copper telephone lines.
ADSL is an asymmetric technology where data transmission occurs in two different frequency bands. The downstream band is used for data downloading and has a higher bandwidth. The upstream band is used for data uploading and has a lower bandwidth. This means that the download speed is higher than the upload speed.
It is a widely used type of internet connection in homes and businesses, suitable for performing basic tasks such as browsing the internet, sending emails, downloading files, and watching videos.
Advantages of ADSL include:
- It utilizes existing copper telephone lines, making installation and maintenance easy.
- It is often more cost-effective than other types of internet connections.
- It provides sufficient bandwidth for performing basic internet tasks.
Disadvantages of ADSL include:
- Copper cables may cause data loss, leading to variable data speeds based on distance.
- ADSL is not as fast as fiber optic internet.
To use ADSL, you need an ADSL modem and an Internet Service Provider (ISP). The ISP will assist you in setting up and managing your ADSL connection.
Learn how to change DNS settings correctly!
What is VDSL?

VDSL stands for Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line. Similar to ADSL, VDSL transmits internet over copper cables. However, VDSL is capable of transferring data at higher speeds compared to ADSL.
The maximum speeds vary depending on the distance and the quality of the cable used. Generally, VDSL is about 10 times faster than ADSL. VDSL makes it ideal for applications such as HD video streaming, online gaming, and other high-bandwidth-demanding tasks.
VDSL may be more expensive than ADSL, but its higher speeds can justify the cost. The advantages of VDSL include:
- High Speed: VDSL is 10 times faster than ADSL, making it ideal for HD video streaming, online gaming, and other high-bandwidth applications.
- Wide Coverage Area: VDSL can be used over longer distances compared to ADSL, extending its reach to a broader area.
- Lower Noise: VDSL has less noise compared to ADSL, providing a more reliable and stable connection.
However, VDSL has some drawbacks, including:
- Higher Cost: VDSL may be more expensive than ADSL.
- Less Compatibility: VDSL is less compatible than ADSL, and some older network devices may not work with VDSL.
If you want to increase your followers, immediately buy Coub followers!
What is VDSL2?

VDSL is a good option for users requiring high speed and extensive coverage. It is particularly well-suited for applications that demand a significant amount of bandwidth, such as HD video streaming and online gaming.
VDSL2, Very-high-bit-rate Digital Subscriber Line 2, is the abbreviation for. It is a DSL technology similar to ADSL but operates at higher speeds. VDSL2 provides broadband internet access using copper cables.
It achieves greater bandwidth by utilizing higher frequencies on copper cables compared to ADSL. This results in faster download and upload speeds. VDSL2 can reach download speeds of up to 100 Mbps and upload speeds of up to 60 Mbps.
VDSL2 is used for various applications, including:
- Internet access
- Video streaming
- Gaming
- Phone services
It provides a way to deliver high-speed internet access using existing copper cable infrastructure, particularly in areas where ADSL is available.
Advantages of VDSL2 include:
- Higher speeds: VDSL2 provides higher download and upload speeds compared to ADSL.
- Better performance: VDSL2 is more resistant to noise and performs better over longer distances.
- More flexibility: VDSL2 can be used for various applications.
Disadvantages of VDSL2 include:
- More expensive: VDSL2 can be more costly than ADSL.
- Less common: VDSL2 is not as widespread as ADSL.
If you want to make money from music, Buy Mixcloud Plays!
Differences Between ADSL, VDSL, and VDSL2
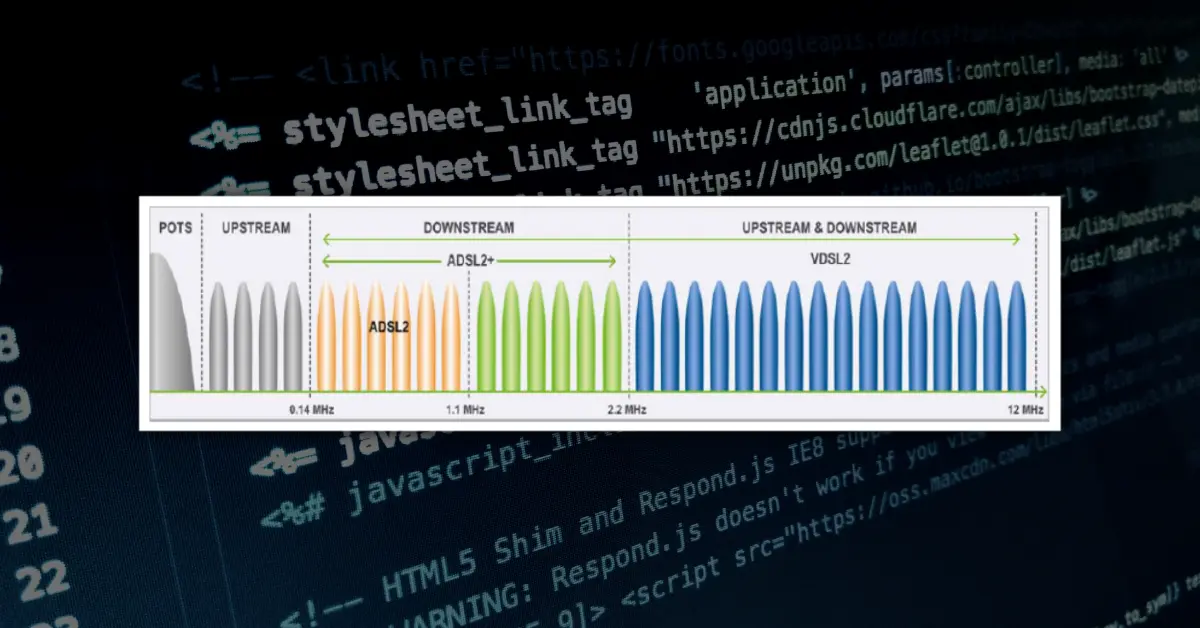
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line), VDSL (Very High Bitrate Digital Subscriber Line), and VDSL2 (Very High Bitrate Digital Subscriber Line 2) are digital subscriber line technologies used for internet access. The fundamental differences among these technologies are outlined as follows:
Speed and Bandwidth
- ADSL: It is an asymmetric technology, meaning that the download speed and upload speed are different. It typically focuses on higher download speeds and can generally offer download speeds ranging from 1 Mbps to 24 Mbps.
- VDSL: It can be configured as asymmetric or symmetric but typically focuses on high download speeds. Download speeds usually range between 50 Mbps and 100 Mbps.
- VDSL2: It offers higher bandwidth and can typically achieve download speeds between 100 Mbps and 200 Mbps. Upload speeds may also be increased.
Distance and Signal Attenuation
- ADSL: Signal attenuation increases as the distance increases, resulting in lower speeds over longer distances.
- VDSL and VDSL2: They perform better over shorter distances, experiencing less speed loss at greater distances.
Infrastructure and Cable Improvements
- ADSL: Generally operates over old copper wire infrastructure.
- VDSL and VDSL2: Can operate over better transmission mediums such as fiber optics or newer copper cables. Therefore, performance can improve with infrastructure upgrades.
Use Cases
- ADSL: Used for low to medium-speed home internet connections.
- VDSL and VDSL2: More suitable for home users requiring higher speeds, small businesses, and areas with heavy internet traffic.
Horizontal and Vertical Speeds
- ADSL: It is an asymmetric line, meaning that download and upload speeds are different.
- VDSL and VDSL2: Can be used in both asymmetric (high download, low upload) and symmetric (similar download and upload speeds) configurations.
What is Fiber Internet?
Fiber internet is a communication technology that provides internet connectivity. It offers higher speeds, more reliable connections, and wider bandwidths compared to traditional copper-based cable infrastructure. Fiber internet relies on the principle of transmitting data at the speed of light through optical fiber cables.
The advantages of fiber internet are as follows:
- High Speeds: Fiber internet typically provides very high data transmission speeds, enabling faster internet-based activities such as file downloads, uploads, video streaming, and online gaming.
- Low Latency (Ping) Times: Fiber internet is known for low latency times, offering a better experience for online games, video conferences, and real-time applications.
- More Reliable Connections: Fiber optic cables are less susceptible to electrical interference, electromagnetic interference, and weather conditions. Fiber internet connections are generally more reliable and stable.
- High Bandwidth: Fiber internet provides wide bandwidths that allow multiple devices to connect simultaneously and facilitate the transmission of large amounts of data.
- Future-Ready Infrastructure: Fiber internet infrastructure is designed to better respond to future broadband needs. Therefore, transitioning to higher speeds with technological advancements can be easily achievable.
















